Orthopedic traumatologists perform expert diagnosis (radiology, laboratory), conservative treatment (drugs, intra-articular injections, PRP therapy, cell technology for regenerative medicine, etc.) and high-tech surgical treatment of knee arthrosis (knee joint) - arthroscopy, endoprosthesis, corrective osteotomy.
One in 10 people over the age of 55 suffer from knee joint disease, which causes disability in one in four cases.
Up to 80% of patients with knee joint disease report a decrease in quality of life.
The functional duration of modern knee endoprostheses is 99% at 10 years, 95% after 15 years, and 90% after 20 years.
Why does knee arthritis occur?
- Most often, the disease develops due to injuries to the knee joint, especially repeated injuries (meniscal injuries, dislocations, fractures, hematomas, etc.).
- Frequent repetitive microtrauma to joints and constant work "on the feet" during athletic training can have a similar effect.
- Excess body weight increases axial loads and damages joints.
- Degenerative dystrophic processes of the joints can also occur after suffering from inflammatory diseases (arthritis due to gout, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis).
- Endocrine diseases, hormonal changes (such as menopause), and metabolic disorders can aggravate pathological changes in joints.
Main symptoms of knee pain
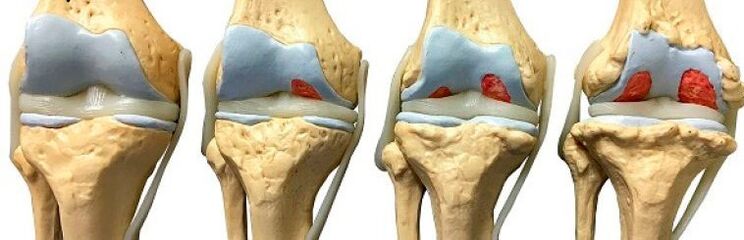
- Grade 1 knee arthrosis - In the initial stage of the disease, periodic pain will occur in the knee joint after exercise (walking, running, standing for a long time), and the pain will disappear after rest.At this stage, there is little joint deformation or limitation of movement;
- Gradually, the pain becomes more frequent and intensified, especially when going up and down stairs, and when starting to walk after sitting for a long time (pain begins);
- Grade 2 knee arthrosis, knee pain persists during exercise and disappears after a long period of rest, and the patient limps when walking;
- There will be a crunching sensation in the joints when moving.Restricted range of motion of the knee joint (severe pain with "full flexion");
- When examining the joint area, you may notice swelling and deformity;
- 3rd degree knee DOA is equivalent to severe knee arthrosis. The joint pain is annoying even at rest, unable to sleep, the range of motion is significantly reduced, the patient walks with bent legs, and the knee joint is obviously deformed (O-shaped or X-shaped legs).
diagnosis
- Investigation and examination by the orthopedic traumatologist revealed classic signs of degenerative dystrophic arthropathy (pain on palpation, limited movement, crepitus, deformity, joint effusion).
- X-rays of the knee joint were performed (to determine X-ray joint space narrowing, presence of osteophytes, subchondral sclerosis) and, if necessary, computed tomography of the joint.
- Articular ultrasound examination can detect thinning of intra-articular cartilage, changes in peri-articular ligaments, muscles, and soft tissues, inflammatory effusion in the joint cavity, changes in the meniscus, etc.
- The most accurate information is provided by magnetic resonance imaging of the knee, which can show changes in cartilage and bone tissue, ligaments, menisci, synovium and thus differentiate between post-traumatic joints of the knee and arthritic and neoplastic processes.
- Diagnostic paracentesis and arthroscopy of the knee joint, as well as laboratory testing of synovial fluid obtained during surgery, are widely used in the diagnosis of joint disorders.
Treatment of knee joint disease
Treatment for knee arthritis depends on the stage of the disease.
conservative
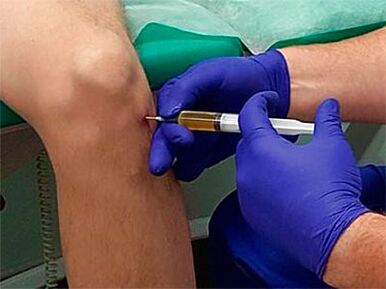
In the early stages of DOA, successful complex conservative treatments are available aimed at relieving inflammation, restoring cartilage, eliminating pain, and restoring full joint function:
- Treatment and protective regime - it is necessary to limit the load on the joints and ensure rest.
- Conservative medical treatment of knee joint disease:
- Use analgesics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and chondroprotectants;
- Topical medications in the form of ointments and gels;
- Intra-articular injection - Injecting a combination of individually selected drugs into the joint, which may include hormone drugs to quickly relieve inflammation, hyaluronic acid drugs to replenish synovial fluid, etc.;
- PRP Therapy - Intra-articular injection of PRP (autologous platelet-rich plasma).
- Regenerative medicine method - intra-articular injection of autologous cells from the stromal vascular part, cells - precursors of cartilage tissue, obtained from the own adipose tissue.
- Massage, physiotherapy, manual therapy.
- Therapeutic physical training and a series of exercises designed to improve blood circulation to the joints and increase range of motion are mandatory.
surgical
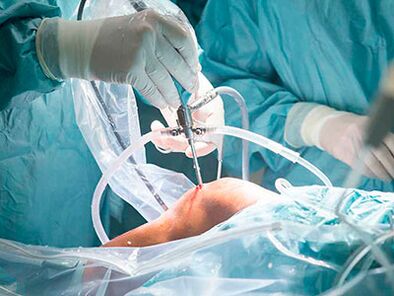
knee arthroscopy
If there are significant changes in the joint (advanced osteoarthritis, traumatic defects), the orthopedic traumatologist performs arthroscopic surgical treatment of the knee joint (meniscal, cartilage surgery, "articular mouse" resection, synovectomy, etc.).
knee replacement surgery
If other treatments fail, we perform knee replacements using modern prostheses from the best manufacturers in the world.This is a proven way to relieve pain, restore mobility and a good quality of life for patients.
Today, there is no point in enduring the pain and inconvenience of joint pain.Modern medical technology can help treat knee arthritis at almost any stage.Contact your doctor and take advantage of the options available.



































